Table of Contents
Toggle4 Most Useful Pressure Types

Pressure, Temperature, Level and Flow are 4 Pillar Process Parameters in the Process Industry. Pressure is one of them. It is important to understand about the concept of Pressure and different type of Pressure in depth.
Concept of Pressure

Do you Know, why knifes are sharpened? Have you ever noticed that nails are always having pointed sharp portion at one end.
If you cut the potato with sharpened side, it is easy to cut the Potato instead of cutting it from unshaped portion of the knife or flat portion of knife, even if the same force is applied. It is equally important to understand how that force is distributed on the surface of impact.
What is Pressure?
Formula of Pressure

The basic formula for pressure is F/A (Force per unit area).
We can Say P = F / A
Where P is Pressure, F is Perpendicular Force and A is Area.
Unit of Pressure

If we consider that the force (in Kg) is exerted on surface of size 1 Cm x 1 Cm, then unit of pressure will be equal to Kg/Cm2. Pressure’s SI Unit is Pascal (Pa), which is equivalent to N/m2.
The Unit Pascal is named after Blaise Pascal (a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic writer), noted for his contributions to hydrodynamics and hydrostatics, and experiments with a barometer.
Example -1
Force = 1 Kg
Side = 1 Cm
Area = Side x Side
Pressure = Force / Area

If we calculate are of the Square of Side 1 Cm x 1 Cm, it will be 1 Cm2.
So, Pressure will be F/A i.e., 1 Kg / 1 Cm2, which will be 1 Kg/Cm2.
Example -2

Force = 8 Kg
Side = 2 Cm
Area = Side x Side
Pressure = Force / Area
It can be derived by dividing each of the side of parts 1 Cm x 1 Cm.
Total 4 Parts of side 1 Cm x 1 Cm can be arrived.
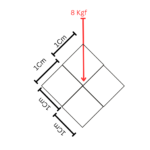

Since, there are total 4 Parts of unit area, we will divide the Force also in 4 equal parts.
So, there will be equally distributed force of 2 Kg on each part (8 / 4 = 2).
Hence, Pressure exerted will be 2 Kg/Cm2 on each portion, based on example 1.
By using the formula straight away, we can calculate the area of Square of 2 Cm as 2 Cm x 2 Cm = 4 Cm2.
So, Pressure will be F / A i.e., 8 Kg / 4 Cm2, which will be 2 Kg / Cm2.
Different Units of Pressure
Pascal (Pa)
KPa (KiloPascal) : 1000 Pa = 1 KPa
Mpa (MegaPascal) : 1000 KPa = 1 MPa
N/m2 : 1 N/m2 = 1 Pa
atm (it is nothing but Standard atmospheres).
Kg/Cm2 or Kgf/Cm2 or
at (at is technical atmospheres).
Bar
mBar : 1 Bar = 1000 mBar
PSI (Pounds per Square inch) or
lb/in2 (lb is short form of Pounds).
14.22334 PSI = Kg /Cm2
mm WC (or mm of Water Column),
This is one of the manometric unit.
10000mmWC = 1 Kg /Cm2.
Inches of Water Column
25.4mm WC = 1Inch WC
mm Hg (or mm of Mercury Column).
This is one of the manometric unit.
Inches of Mercury Column
: 25.4mm Hg = 1Inch Hg
Torr (1 torr is equal to 1mm Hg)
Different Types of Pressure
Atmospheric Pressure

Atmospheric Air of Earth is surrounded by layer of Gases. These gases exert pressure on Atmospheric Air, which is called Atmospheric Pressure.
Atmospheric Pressure value is approx. 101325 Pa or 1.01325 Bar or 1 Kg/Cm2 or 760mm Hg.
Atmospheric pressure is maximum at sea level (i.e., 760mm Hg) and decreases while moving above sea level.
Absolute Pressure
Total force exerted on per unit area of the substance is called absolute Pressure.
This is the pressure that changes, as the location changes because Atmospheric Pressure changes with respect to sea level.
As we go at higher sea level, value will be reduced.
Gauge Pressure
Gauge pressure is nothing but the difference between absolute pressure and atmospheric pressure. Gauge pressure is also known as relative pressure. The measured pressure is compared to the standard atmospheric pressure at the sea level i.e., 1 Kg/Cm2 only.
The measured value can be both positive and negative. If the Gauge pressure value is positive, it is termed called Pressure and If the gauge pressure value is negative, it is called vacuum and if it is -1 Kg/Cm2, it is called full Vacuum.
Pressure Gauges are used to measure Gauge Pressure. Pressure Gauges can be provided with Unit as required by customers.
Differential Pressure
Differential pressure is a type of gauge pressure that shows the difference between the two pressures. It helps to measure the pressure difference between two different points and is normally used for flow and level measurement applications.
Differential Pressure Gauges are used to measure Differential Pressure.
Relation between Atmospheric, Absolute and Gauge Pressure

Absolute Pressure (Pabs) is equal to sum of Gauge pressure (Pg) and Atmospheric Pressure (Patm), so we can say Pabs = Pg +Patm
How to represent unit for Gauge pressure and Absolute Pressure
Kg/Cm 2 (g), Bar (g), PSI (g) for Gauge Pressure and
Kg/Cm 2 (a), Bar (a), PSI (a) for Absolute Pressure.
Conclusion
We have explained about the pressure in this write-up and now it is important to understand about the instruments to be used for measurement of Pressure.
Various types of Instruments are available to measure the pressure of Pipeline, vessels, tanks etc., however, it is important to select the correct instrument based on the media, pressure, temperature, viscosity etc.

Pingback: Pressure Gauges and 4 most important type of Pressure Gauges - LK Industrial Solutions
Pingback: 172 Years of Precision - Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge - LK Industrial Solutions